WebMolecule Program Group Project
Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
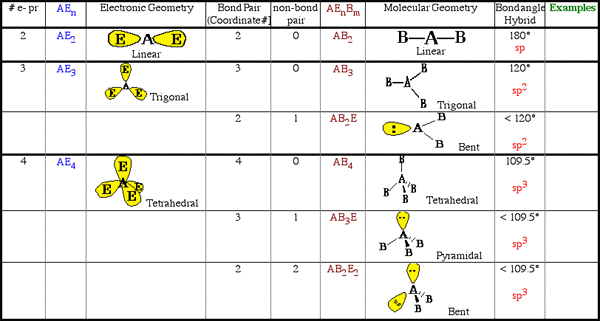
Direction
Using WebMolecules Internet Program.
To view the moleucles using the WebMolecule Program over the Internet you will need the VRML Plug-in. and the Chimie Plug-in. Please click on the link and download the plugin to your browser.I. # Electron Pair - 2
1. Write the Lewis Dot structure for N3- . (Inorganics, sodium azide)2. Count how many electron-pair regions around the central atom.
3. How many of these are electron pairs and how many are bonded atoms?
4. Depending on bonding pair, take these many red balloons from the balloon bag. Take as many white balloons that corresponds to the number of non-bonded electrons around the central atom. If there are no balloons use the molecular modeling kit provided.
5. Tie these balloons together and answer the following questions:
a. What is the designated AEn ? system. What is the electronic geometry ?b. What is the designated ABmEn ? system. What is the molecular geometry ?
c. Use the WebMolecule Website to find the structure so sodium azide. Is the molecule consistent with your prediction ? Draw a sketch of the molecule from the screen display.
d. Is the molecule symmetric. If so, is it polar or nonpolar ?
II Do the same exercise for the following:1 Electronic Pair - 3a . # Electron Pair - 3: Start with the Lewis structures of CHFO (Organic Aldehydes: Formyl Fluoride)2 Electronic Pair - 3b. # Electron Pair - 3: Start with the Lewis structures of FNO (Inorganics: Nitrosyl fluoride or nitroxyfluoride)
a # Electron Pair - 4: Start with the Lewis structures of CH2F2 (Inorganics Halocarbons: CFC's: Difluoromethane)b # Electron Pair - 4: Start with the Lewis structures of PH3 (Inorganics Halocarbons: Phosphine)
c # Electron Pair - 4: Start with the Lewis structures of H2S (Inorganics Halocarbons: Hydrogen sulfide)
III. Look up the following in the WebMolecule Website and determine the following:
a) the geometry around each central atom
b) the bond angle around each central atom
c) the hybridization, to all the central atoms in the molecule.1) Organic: Isocyanide acid CHNO
2) Organic: Nitramide H2N2O2
2) Inorganic: Sulfamide (sulfuryl amide) H4N2O2S
IV. Your CommentsUse the different "View" modes in the WebMolecule program. Summary each "View" mode and offer your comments of about the WebMolecule Program.
Back to Top Back to Course Information Back to FOG Home page
Using WebMolecules Internet Program
|
Sample View of WebMolecule Internet Program